| Author: | K.H. Erickson | ISBN: | 9781311206992 |
| Publisher: | K.H. Erickson | Publication: | January 13, 2014 |
| Imprint: | Smashwords Edition | Language: | English |
| Author: | K.H. Erickson |
| ISBN: | 9781311206992 |
| Publisher: | K.H. Erickson |
| Publication: | January 13, 2014 |
| Imprint: | Smashwords Edition |
| Language: | English |
Microeconomics: A Simple Introduction offers an accessible guide to the central principles and ideas of microeconomics, with over 50 diagrams included to illustrate the analysis.
Understand opportunity cost, diminishing returns, demand and supply, the market equilibrium, market failure, adverse selection and moral hazard. Learn how to calculate price and income elasticities.
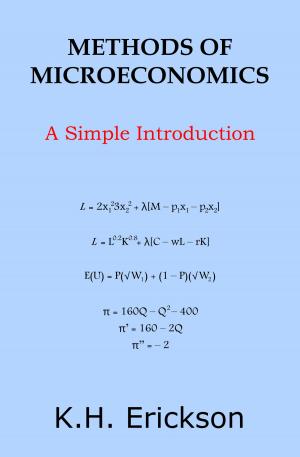
Consumer theory explores budget constraints, indifference curves, marginal rate of substitution, utility maximization, Hicks and Slutsky income and substitution effects, and Samuelson’s revealed preference theory.
Firm theory examines production factors, Cobb-Douglas and other production functions, returns to scale, isoquant curves, isocost lines, cost minimization, profit maximization, Lerner index, and differentiation to derive a marginal revenue curve.
Perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly are explained. Monopoly welfare effects are shown, with oligopoly models of kinked demand, cartels, dominant price leadership, Cournot and Bertrand.
Game theory investigates duopoly and battle of the sexes games, assessing them with dominance and credible threats.
Microeconomics: A Simple Introduction offers an accessible guide to the central principles and ideas of microeconomics, with over 50 diagrams included to illustrate the analysis.
Understand opportunity cost, diminishing returns, demand and supply, the market equilibrium, market failure, adverse selection and moral hazard. Learn how to calculate price and income elasticities.
Consumer theory explores budget constraints, indifference curves, marginal rate of substitution, utility maximization, Hicks and Slutsky income and substitution effects, and Samuelson’s revealed preference theory.
Firm theory examines production factors, Cobb-Douglas and other production functions, returns to scale, isoquant curves, isocost lines, cost minimization, profit maximization, Lerner index, and differentiation to derive a marginal revenue curve.
Perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly are explained. Monopoly welfare effects are shown, with oligopoly models of kinked demand, cartels, dominant price leadership, Cournot and Bertrand.
Game theory investigates duopoly and battle of the sexes games, assessing them with dominance and credible threats.